What is an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)?
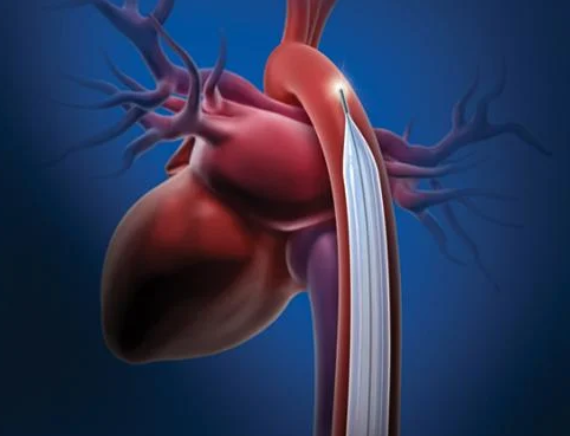
The intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a device that helps the heart pump blood more effectively. It involves a balloon that is placed in the aorta, the large artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The balloon inflates and deflates in sync with the heartbeat to assist with blood flow and reduce the heart's workload.
How does an IABP work?
The IABP works by:
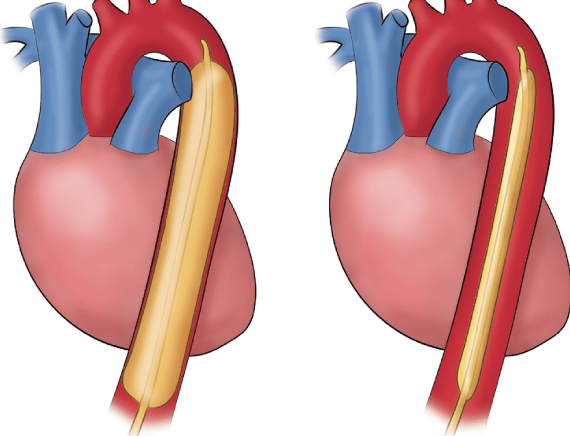
- Inflation: The balloon inflates during diastole (when the heart is resting between beats). This increases blood flow to the coronary arteries and reduces the heart's workload.
- Deflation: The balloon deflates just before systole (when the heart is contracting). This creates a vacuum effect that helps blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta, improving overall cardiac output.
What are the indications for using an IABP?
Indications for IABP include:
- Cardiogenic Shock: Severe condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Severe Heart Failure: When the heart cannot pump effectively despite medication.
- High-Risk Cardiac Procedures: To support the heart during procedures such as coronary angioplasty.
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack): Especially in cases with significant heart failure or compromised cardiac function.
What are the benefits of an IABP?
Benefits of using an IABP include:
- Increased Cardiac Output: Helps to improve the heart’s ability to pump blood.
- Reduced Myocardial Oxygen Demand: Decreases the workload of the heart and reduces the oxygen requirement of the heart muscle.
- Improved Coronary Blood Flow: Enhances blood flow to the heart muscle during diastole.
What are the risks and complications associated with IABP use?
Potential risks and complications include:
