
What is graft angioplasty?
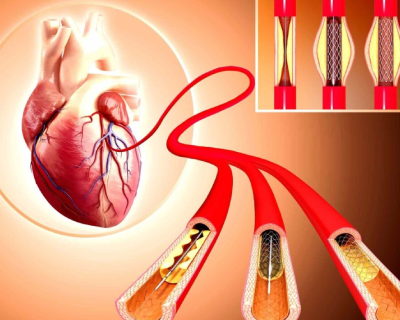
Graft angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open up narrowed or blocked arterial grafts, which are used to bypass blocked arteries. The procedure involves using a balloon catheter to dilate the blocked or narrowed area of the graft, and sometimes placing a stent to keep it open.
Why is graft angioplasty performed?
- Relieve Blockages: Open up grafts that have become narrowed or blocked over time.
- Improve Blood Flow: Restore adequate blood flow through the graft to the heart or other organs.
- Manage Symptoms: Alleviate symptoms such as chest pain (angina) or shortness of breath caused by graft blockage.
- Prevent Heart Attack: Reduce the risk of a heart attack by ensuring proper blood flow through the graft.
How is graft angioplasty performed?
- Preparation: The patient is given a sedative and local anesthesia. An intravenous (IV) line is placed for medications and fluids.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or wrist, and advanced to the graft.
- Angiography: Contrast dye is injected through the catheter to visualize the blocked graft using X-ray imaging.
- Balloon Angioplasty: A balloon-tipped catheter is positioned at the site of the blockage within the graft and inflated to widen the narrowed area.
- Stent Placement (if needed): A stent may be inserted to support the graft and keep it open.
- Completion: The catheter is removed, and the insertion site is closed.
What are the indications for graft angioplasty?
- Graft Stenosis: Narrowing of a previously implanted graft due to plaque buildup or restenosis.
- Angina: Persistent chest pain or other symptoms despite treatment.
- Graft Failure: Poor function or performance of a graft in delivering blood to the heart.
What are the risks and complications associated with graft angioplasty?
- Bleeding: At the catheter insertion site or internally.
- Infection: At the site of catheter insertion or within the graft.
- Graft Dissection: Tear in the graft or adjacent artery wall.
